Hazard Preventions
HAZOP
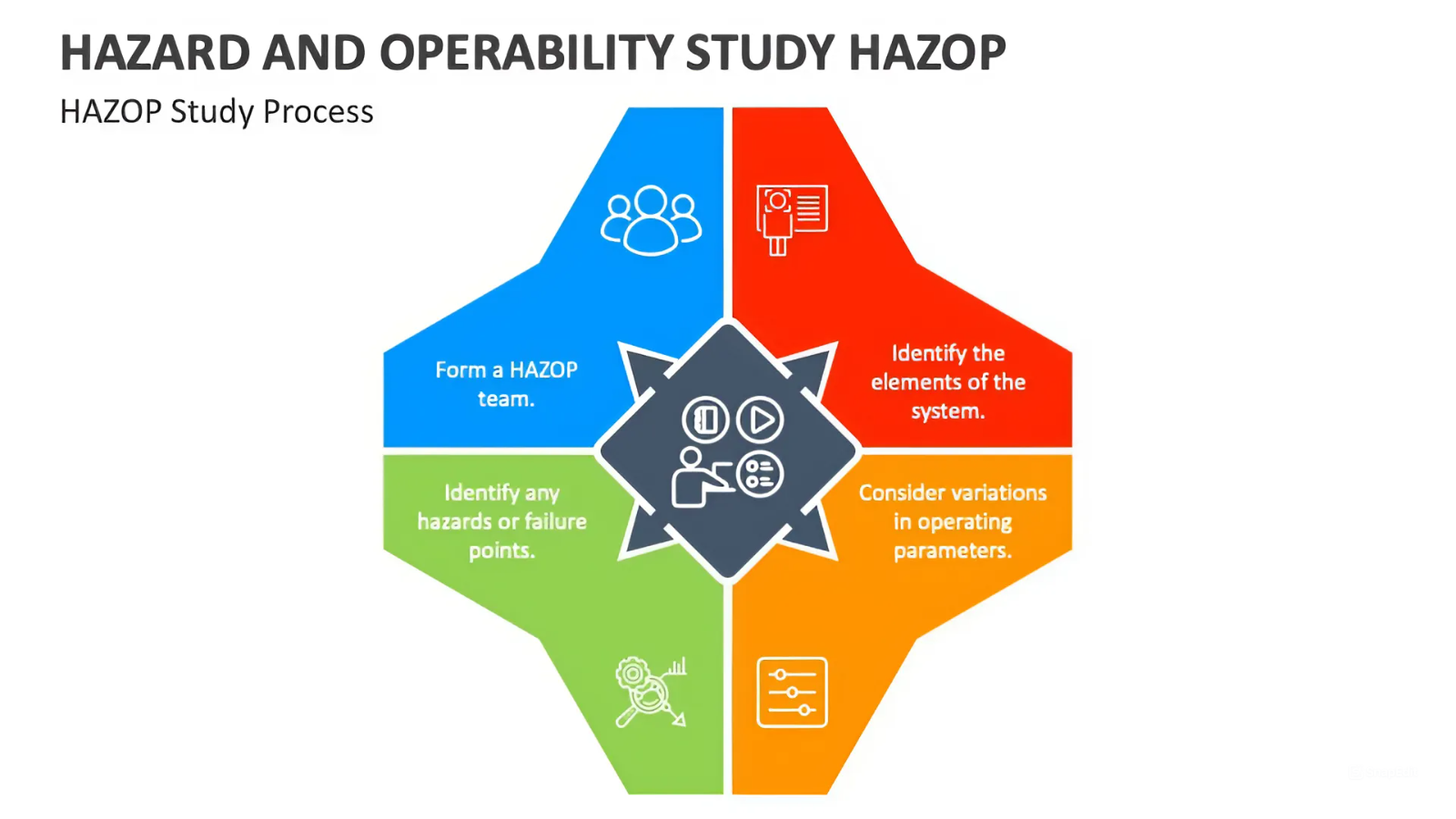
HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) is a structured, team-based method that systematically analyzes potential hazards and operability issues in a chemical process by considering deviations from design intent.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy – A Classic Example of Safety Neglect
Bhopal is a painful reminder that neglecting safety comes at a devastating cost.
Detection and Identification
This process involves identifying potential hazards, assessing their risks, and implementing measures to prevent or mitigate them. Hazard identification can be achieved through various methods such as process hazard analysis, safety audits, and incident investigations. Once hazards have been identified, risk assessment tools such as hazard and operability (HAZOP) studies, failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), and fault tree analysis (FTA) can be used to evaluate the severity of the risks and prioritize preventive measures. Prevention measures can include engineering controls such as safety interlocks and pressure relief devices, administrative controls such as operating procedures and training, and personal protective equipment (PPE). Effective hazard identification and prevention require a comprehensive and systematic approach, and continuous improvement to ensure the safety of chemical processes.
| Aspect | HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) | LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify potential hazards and operability issues systematically | Evaluate the adequacy of existing protection layers for specific hazards |
| Type of Analysis | Qualitative (can be semi-quantitative) | Semi-quantitative to quantitative |
| Focus | Process deviations, causes, consequences | Risk assessment of specific hazard scenarios |
| Output | List of deviations, causes, consequences, safeguards, and recommendations | Risk ranking, need for additional protection layers, and SIL targets |
| Inputs Required | P&IDs, process knowledge, operating procedures | Specific scenarios (often from HAZOP), frequencies, IPL effectiveness |
| Facilitation | Typically facilitated by a multidisciplinary team | Often facilitated by safety or risk analyst with team input |
| Use of Scenarios | Broad exploration of what can go wrong | Focused evaluation of selected scenarios |
| Detail Level | High-level brainstorming of process issues | Detailed risk quantification of specific events |
| Risk Evaluation | Based on team judgment | Uses numerical estimates (e.g., frequency, probability, risk matrix) |
| Standards Referenced | IEC 61882, OSHA 1910.119 | IEC 61511, CCPS LOPA Guidelines |
| Typical Outcome | List of required actions, design changes, or safeguards | Decision on whether existing layers are sufficient or more needed |
| When Used | Early in design or during major modifications | After HAZOP to assess the risk of critical scenarios |
| Tool Dependency | Checklist- and guideword-based | Risk matrix, consequence severity, IPL credit calculations |